Table Of Content

Hair grows everywhere on the external body except for mucus membranes and glabrous skin, such as that found on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, and lips. The most important function of hair in mammals is that of insulating against cold by conserving body heat. The differing colours and colour patterns in hair coats can also serve purposes of camouflage and of sexual recognition and attraction among the members of a species. Specialized hairs called vibrissae, or whiskers, serve as sensory organs for certain nocturnal animals. The specially modified hairs of the porcupine are called quills and serve defensive purposes. While your hair color can change throughout your life, your hair follicle, which is part of your skin, is the same color as your natural skin tone.
What is a hair follicle?
The skin of the scalp is highly innervated with blood vessels and sensory receptors known as Pacinian corpuscles. The corpuscles are egg-shaped and comprise many concentric rings of tissue layers. They are innervated with a free nerve ending and therefore work as deep pressure receptors to external stimuli. These layers can easily be remembered using the handy mnemonic SCALP.
Microanatomy of Telogen Phase Hair
While the features observed in scattering experiments are well known, the molecular architecture of the intermediate filaments is still under discussion (Rafik, Doucet & Briki, 2004). Supercoiled coiled-coils or models that involve straight dimers with different numbers of coils are being discussed. Human scalp hair is a bio-synthesized material that has a complex internal structure.
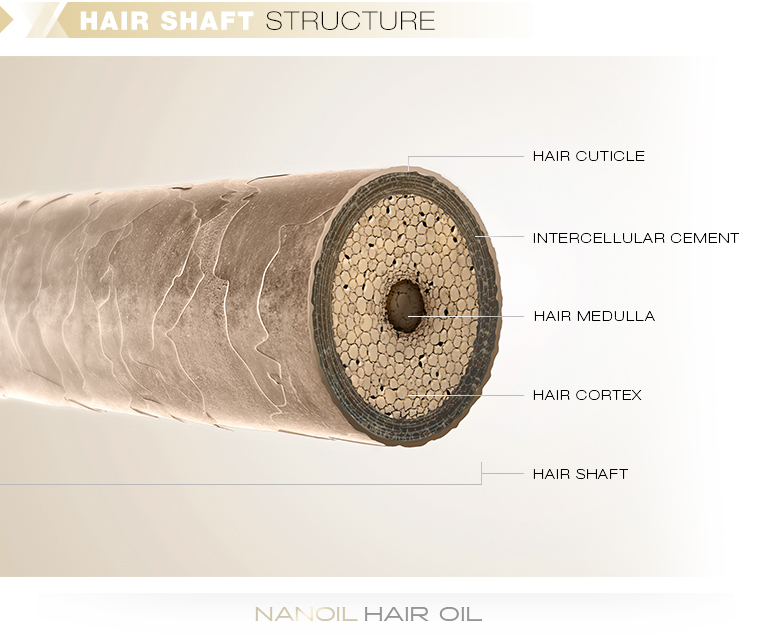
The Biology, Structure, and Function of Hair
The inception of anagen phase is presented by the onset of the mitotic activity in the secondary epithelial germ located between the club hair and dermal papilla in telogen hair follicle [5, 16]. The anagen is the active growth phase in which the follicle enlarges and takes the original shape and the hair fiber is produced. Outer root sheath (ORS) extends from the epidermis at the infundibulum and continues to the hair bulb and its cells change considerably throughout the follicle.
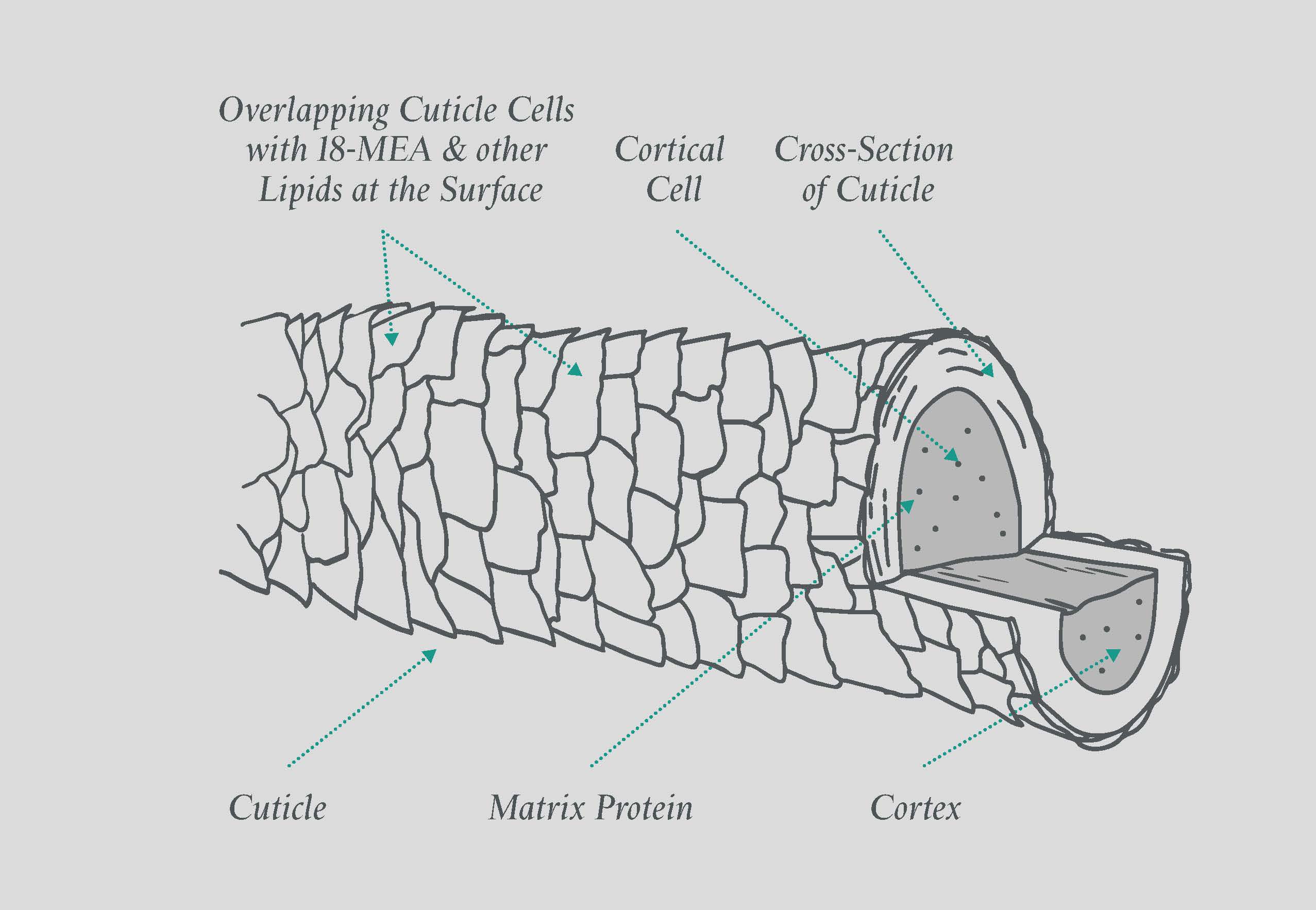
In particular, straight hair tends to have symmetrical distribution of the ortho- and paracortices whereas curly hair tends to have a non-symmetrical distribution of these cortical cells (Kajiura et al., 2006). Most of the cortical cells are composed of a protein known as keratin (Robbins, 2012). The purpose of this study is to use X-ray diffraction to analyze the structure of human scalp hair for individuals with differing characteristics.
Microanatomy of Catagen Phase Hair
The base of the follicle bulges, forming a hair bulb which surrounds the hair papilla. The bulb is invaginated by connective tissue known as dermal papilla. The dermal papilla contains many tiny blood vessels and nerve projections.
The other is made up of longitudinal A-delta fibers and circular C fibers and encircle the midsection of the hair follicle, between the isthmus and the sebaceous gland. Nearby nerves also innervate the proximal arrector pili muscles. The outermost layer of cells is known as the external root sheath.
Nonreactive Paths to Internal Changes: Modifying Hair's Structure from the Inside, Part 2 - Cosmetics & Toiletries
Nonreactive Paths to Internal Changes: Modifying Hair's Structure from the Inside, Part 2.
Posted: Fri, 10 Jun 2016 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Hair structure
The body has different types of hair, including vellus hair and androgenic hair, each with its own type of cellular construction. The different construction gives the hair unique characteristics, serving specific purposes, mainly, warmth and protection. All natural hair colors are the result of two types of hair pigments. Both of these pigments are melanin types, produced inside the hair follicle and packed into granules found in the fibers.
Do hair follicles heal after an injury and will my hair grow back?
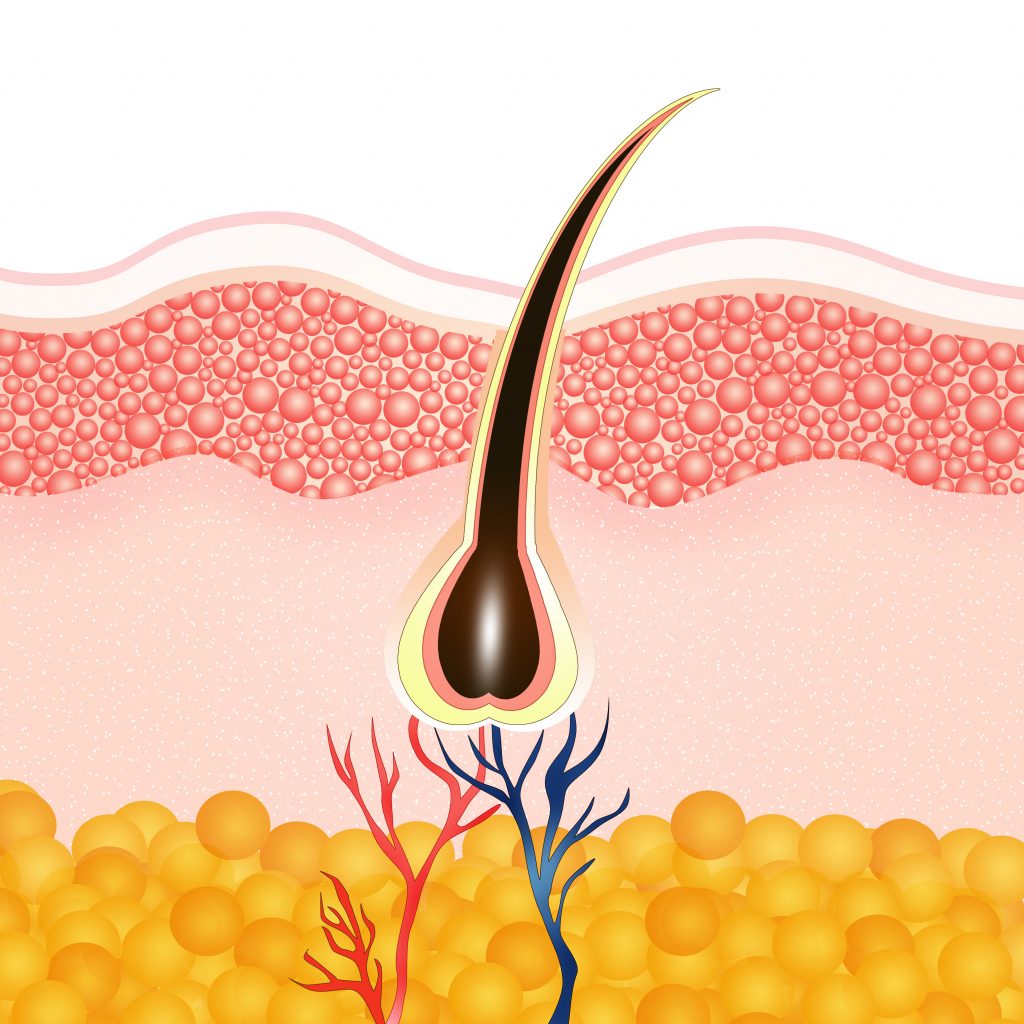
As the cells are pushed upward from the follicle’s base, they become keratinized (hardened) and undergo pigmentation. If you damage your hair follicles after an injury, they can repair themselves and your hair will grow back. It could take up to four years before you see new hair growth out of damaged hair follicles, depending on the severity of your injury. Frequent injuries to your skin and hair follicles can produce scars, which make growing hair difficult. Hair that does grow is thinner and more fragile hair than normal.
Facial hair, and especially eyelashes, eyebrows and body hair grows at a slower pace. The shaft is the visible part of the hair that sticks out of the skin. The hair root is in the skin and extends down to the deeper layers of the skin. It is surrounded by the hair follicle (a sheath of skin and connective tissue), which is also connected to a sebaceous gland.
The opposite actions occur when the body is too warm; the arrector muscles make the hair lie flat on the skin which allows heat to leave. The rate of hair loss may increase noticeably if the hair roots are damaged during the growth phase or if a lot of hairs go into the resting phase at the same time. If no new hair grows and replaces the hair, that part of the skin becomes bald.
The three features above were observed in all individuals in Fig. The underlying molecular structures will be quantitatively analyzed in the next section (Quantitative analysis of scattering results). We note that additional features are seen in some of the measurements in Fig. 1, mainly in the broad membrane ring at around 1.5 Å-1 which indicates a difference in molecular composition of the cell membrane complex between individuals. Thus hair follicle IP is limited to the proximal epithelium of anagen hair follicles.
The cut-out at the middle of the apparatus is where scattering occurs on the hair sample. The cardboard apparatus is then mounted vertically onto the loading plate of the Biological Large Angle Diffraction Experiment (BLADE) using sticky putty as shown in Fig. All hair samples were measured at room temperature and humidity of 22 °C and 50% RH. Coba Academy has been training beauty professionals for over 50 years.
Research leads to new discoveries about structure of human hair - Phys.org
Research leads to new discoveries about structure of human hair.
Posted: Thu, 28 Jan 2016 08:00:00 GMT [source]
In the infundibulum, it resembles epidermis, whereas in the isthmus level, ORS cells begin to keratinize in a trichilemmal mode. Keratinocytes in the ORS form the bulge area at the base of the isthmus. At the lower tip of the hair bulb it consists of a single layer of cuboidal cells, becoming multilayered in the region of the upper hair bulb.

No comments:
Post a Comment